Brief overview of AI in healthcare
AI (artificial intelligence) in healthcare uses machine learning, natural language processing, enhanced pattern recognition, and other technologies to provide patient care and healthcare professional experiences. Today, AI can be used to enhance every phase of a patient’s journey.
It can assist doctors in quicker and more accurate diagnosis and treatment, can design a personalized treatment plan for patients using historical health data, and can manage resources of healthcare professionals effectively. It supports robotic surgery, improves clinical documentation, and provides predictive analysis, streamlining scheduling, billing, and responding to patient inquiries. The capabilities and possibilities seem endless.
It can assist healthcare professionals in many ways, but can it ever replace them? No, it cannot and it should not. In this article we will explore how much of AI in healthcare is too much in clinical diagnosis and treatment.
The Debate: AI Assistance vs. Human Expertise
Several studies show that our physical well-being is deeply connected with our mental well-being. Positive emotions can aid the recovery phase and sometimes can reduce the risk of physical ailments; this has been proved scientifically. Empathy and compassion are the cornerstones of the doctor-patient relationship. When a doctor examines us, explains our illness, and the course of treatment that he has decided to provide us makes us feel comfortable. The human doctor’s body language, his emotions, and his reassurance and confidence towards the treatment plan and its outcome—providing a sense of security and trust to the patient—create positive emotions—this is an essential ingredient in the healing process. This humane factor of empathy and compassion is missing in AI-assisted care.
However, we cannot deny the fact that healthcare providers are under pressure throughout the world.
In western countries, where the aging population is growing, there is a shortage of doctors, and often there is dissatisfaction with the amount of time a doctor spends with their patient.
Similarly, in India, especially in rural India, there is a scarcity of qualified, specialized healthcare providers. This is where AI-augmented treatment can lessen the burden and dependency on healthcare providers. AI can streamline the process to increase the overall efficiency of the system. Please note here we are talking about embedding the healthcare system with AI-powered tools; we are not suggesting replacing healthcare providers. AI augmentation will save our doctors’ time, which they can use in providing quality time with their patients.
Role of AI in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Patient Triage
Like every other industry, AI in healthcare is also rapidly growing and evolving; it has crossed the initial step of adoption. Now it is getting integrated widely into the clinical ecosystem. Let us explore some of the areas where AI is being widely used for providing better healthcare.
1. Clinical Diagnosis—The aim of clinical diagnosis is to assess the patient’s condition by evaluating the patient’s vitals (body temp, SPO2, heart rate, and BP), clinical and pathology results, past medical history, lifestyle habits, environmental influences, and genetic information. By analyzing all these aspects, a healthcare professional can identify the root cause of the ailment and can determine the most effective treatment plan that might suit that specific patient. The more of this information a doctor can assess, the more accurately he can diagnose. Now imagine a human doctor having to assess and analyze all this information within a limited time and arrive at a conclusion. Wherein an AI algorithm can analyze all this information quickly and more accurately with minimal errors—something that would be time-consuming and error-prone because of human limitations.
Equipped with AI-generated consolidated patient reports, a healthcare provider will be in a position to make a better and more precise decision quickly.
2. Treatment Recommendation: AI can be leveraged to aid healthcare providers in providing better care and personalized treatment plans to their patients. Let’s explore a few of these areas:
a. AI algorithms can assess patient-specific data and can generate personalized treatment recommendations, which a healthcare provider can validate or can take cues from.
b. Oncology—This is one area where AI-aided treatment is revolutionizing. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of datasets to assess tumor characteristics, genetic profiles, and patient data to predict how a patient might react to certain therapies, and this helps the oncologist to recommend and decide on a specific treatment plan for a patient that will be effective with fewer side effects. With the help of AI, oncologists can plan targeted chemotherapy and radiotherapy, which are more precise and effective.
c. AI-driven technology is providing promising geriatric care. AI-powered wearables can keep track of the vitals of geriatric patients and send alerts to caregivers in emergency conditions. AI-powered monitoring can detect falls and can help Alzheimer’s patients with navigation. There are tools that can help geriatrics to overcome social isolation.
3. Patient Triaging—AI algorithms are trained on historical health data of patients to assess the severity of the condition. AI can be used to automate some aspects of triaging in hospitals, like collecting patient data, assessing the condition, and assigning triage levels, so that professionals can focus on more complex tasks.
AI, Data Privacy, and Trust in Healthcare
AI algorithms are trained on a large amount of data. In healthcare, these algorithms need access to large amounts of patient data, which are highly sensitive and deeply personal. To protect patients’ confidentiality and to ensure ethical use of AI, it is extremely important to have a robust security system in place.
Any kind of cyberattack or data breach can cause serious consequences, putting patients’ privacy at risk. The “black box” nature of AI algorithms can make patients and healthcare providers uncomfortable about putting their trust in it. They may question the accuracy and reliability of its diagnostics and treatment recommendations. Healthcare AI systems need to carefully address and minimize these risks. They should implement robust data security measures like data encryption, access control, and periodic audits. For transparency and trust, they should develop algorithms that are transparent and explainable.
Public Perception: Are Patients Comfortable with AI in Healthcare?
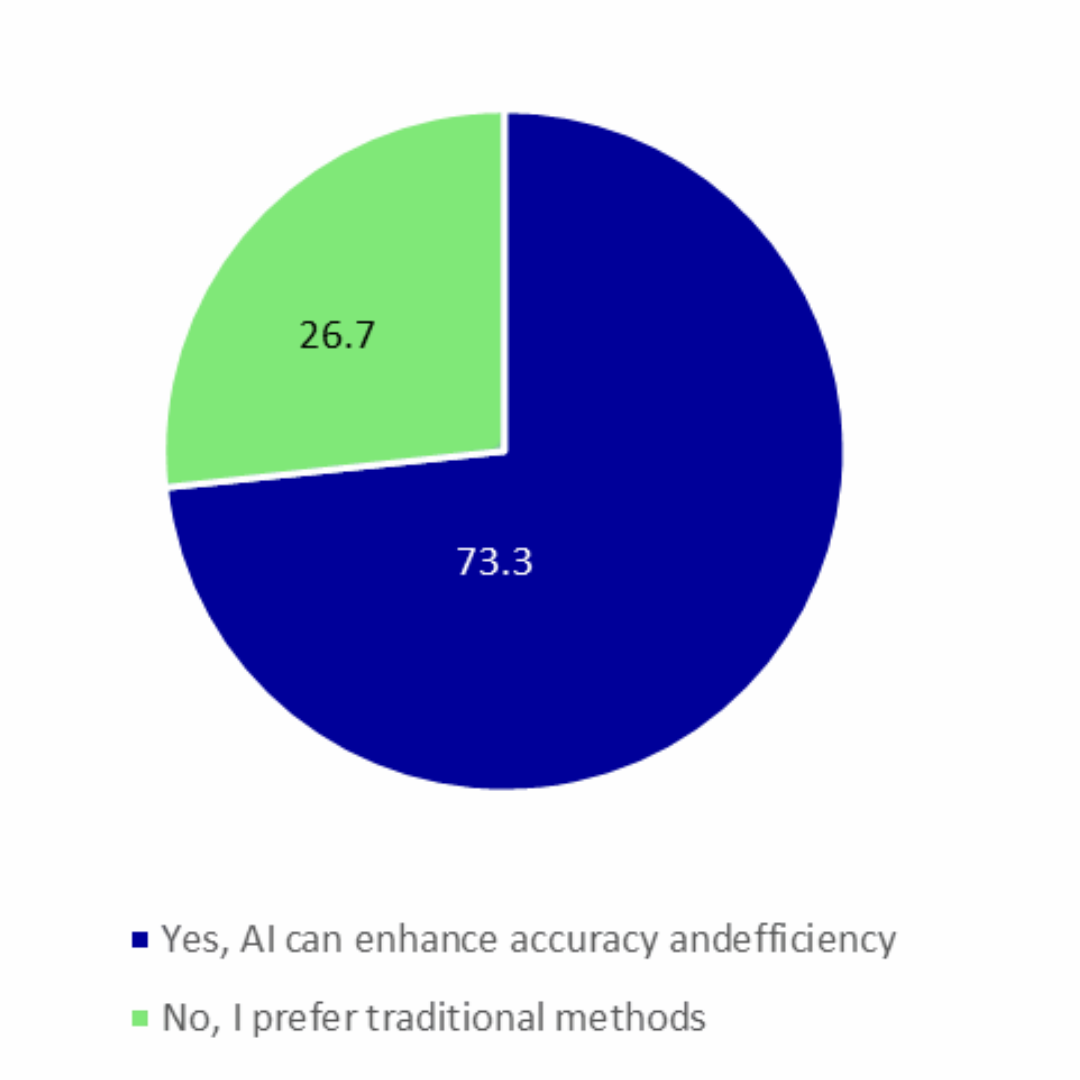
Would you trust AI to assist in providing an initial diagnosis before consulting a doctor?
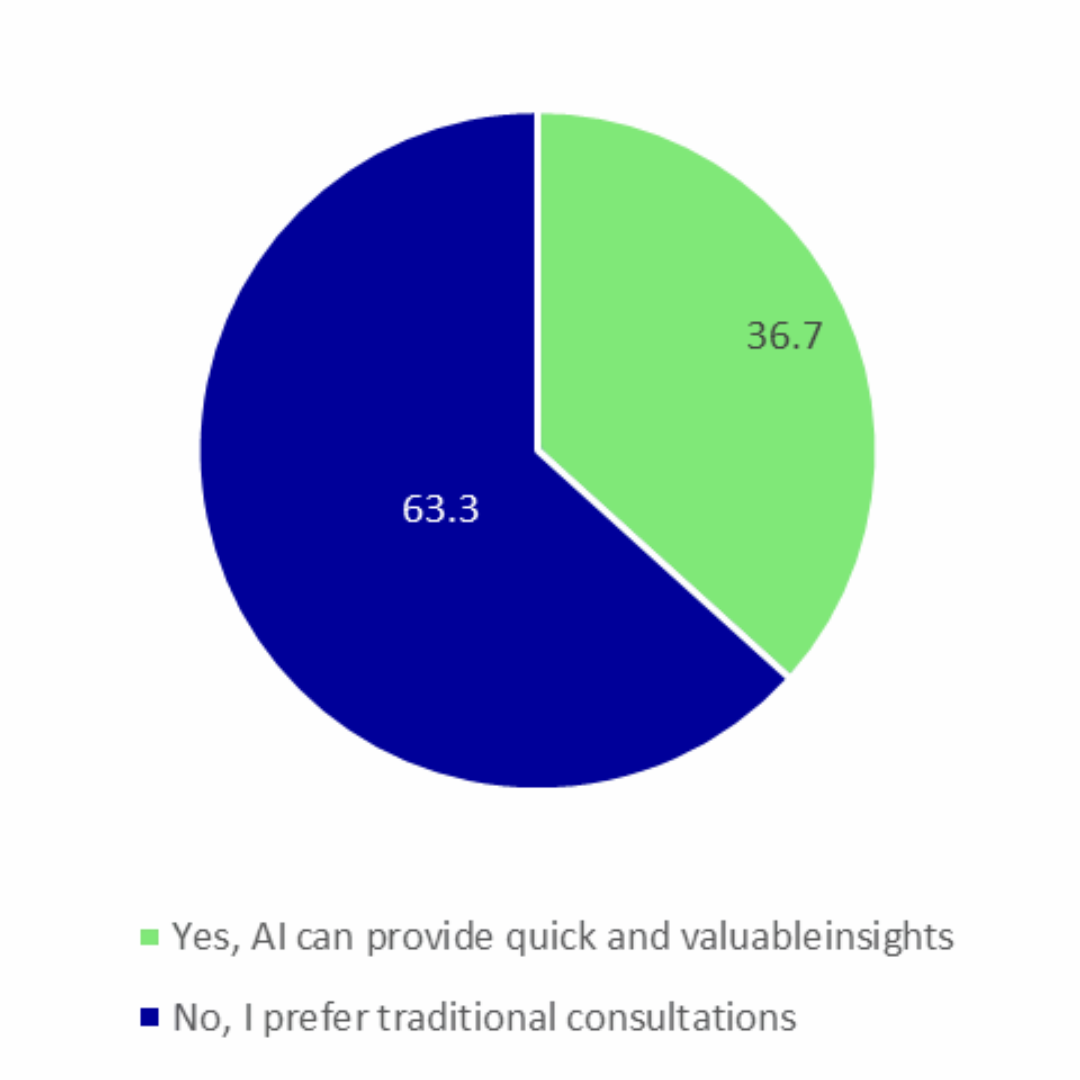
Would you be open to using an AI-powered health assistant for everyday medical advice and health tracking?
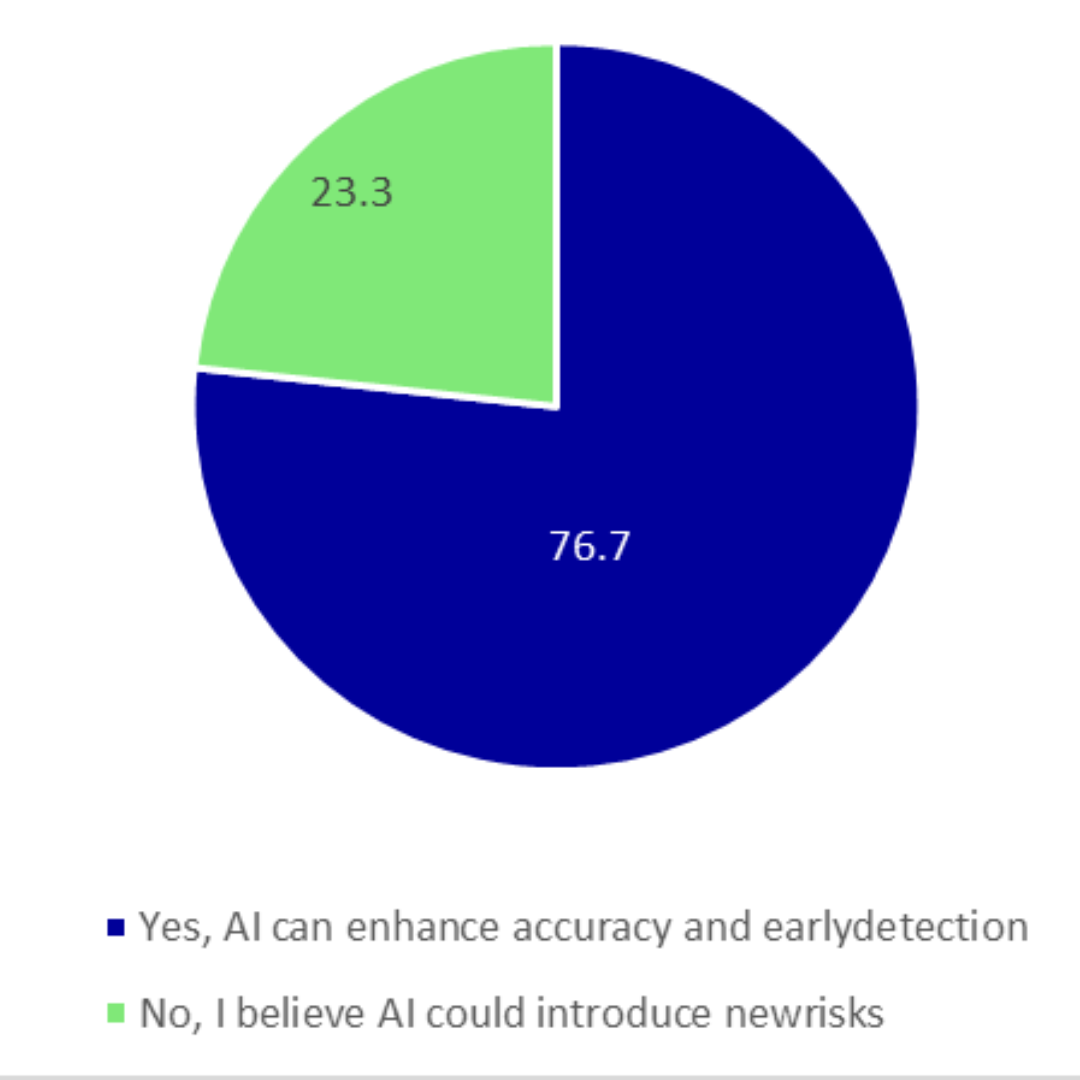
Do you believe AI can reduce medical errors and improve patient safety?
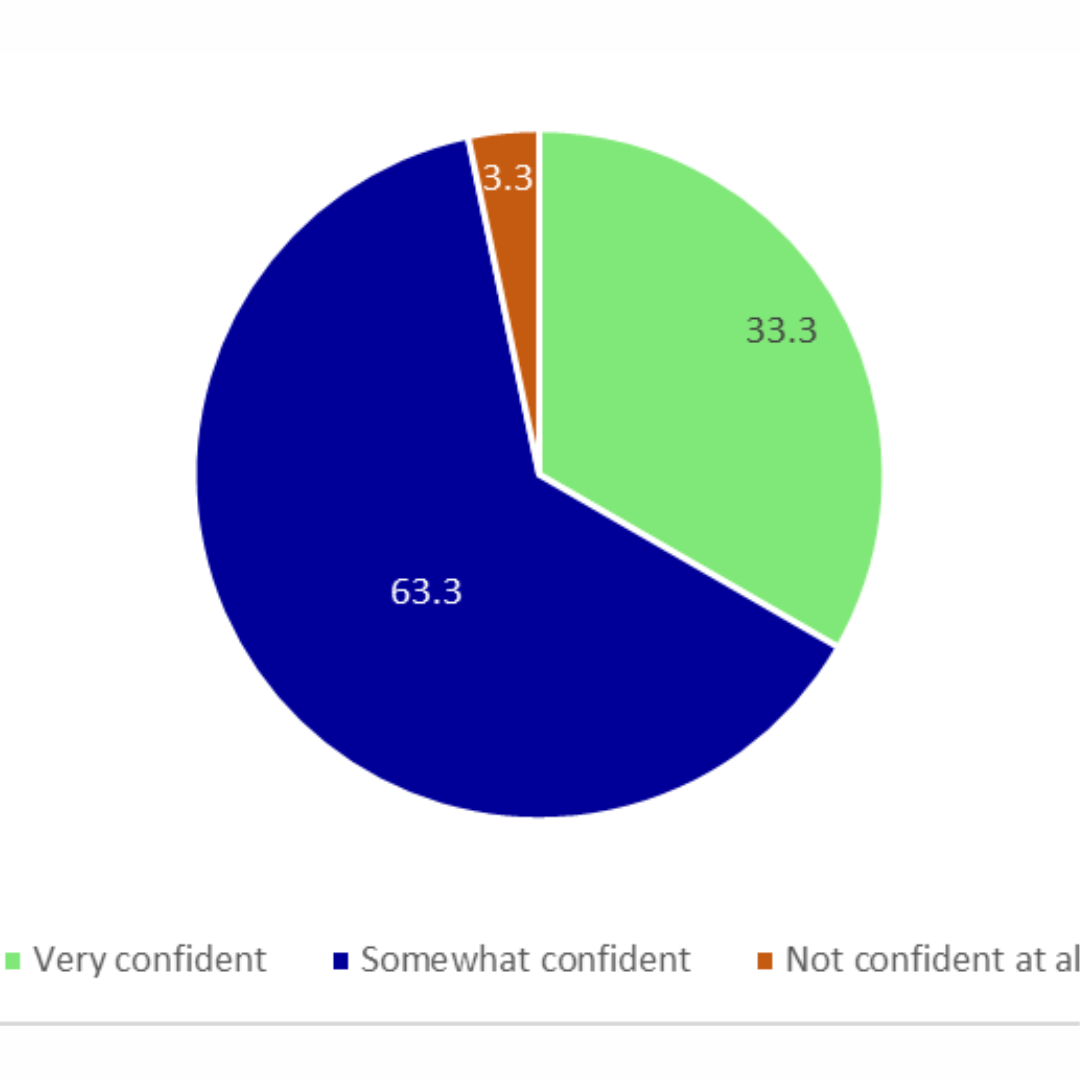
If AI recommends a treatment plan alongside your doctor, how confident would you feel?
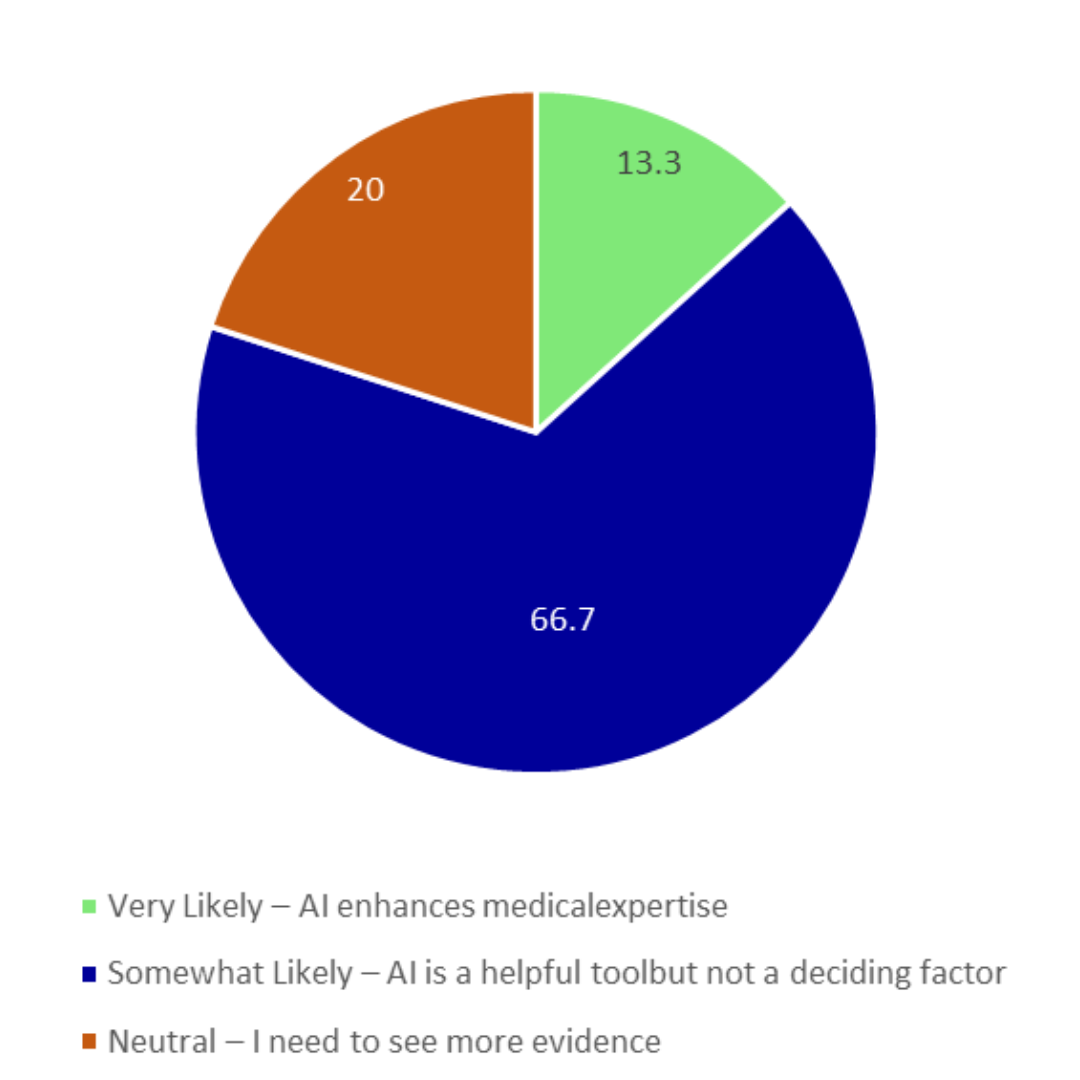
Would you prefer AI-powered remote consultations over in-person visits for minor illnesses, saving time and resources?
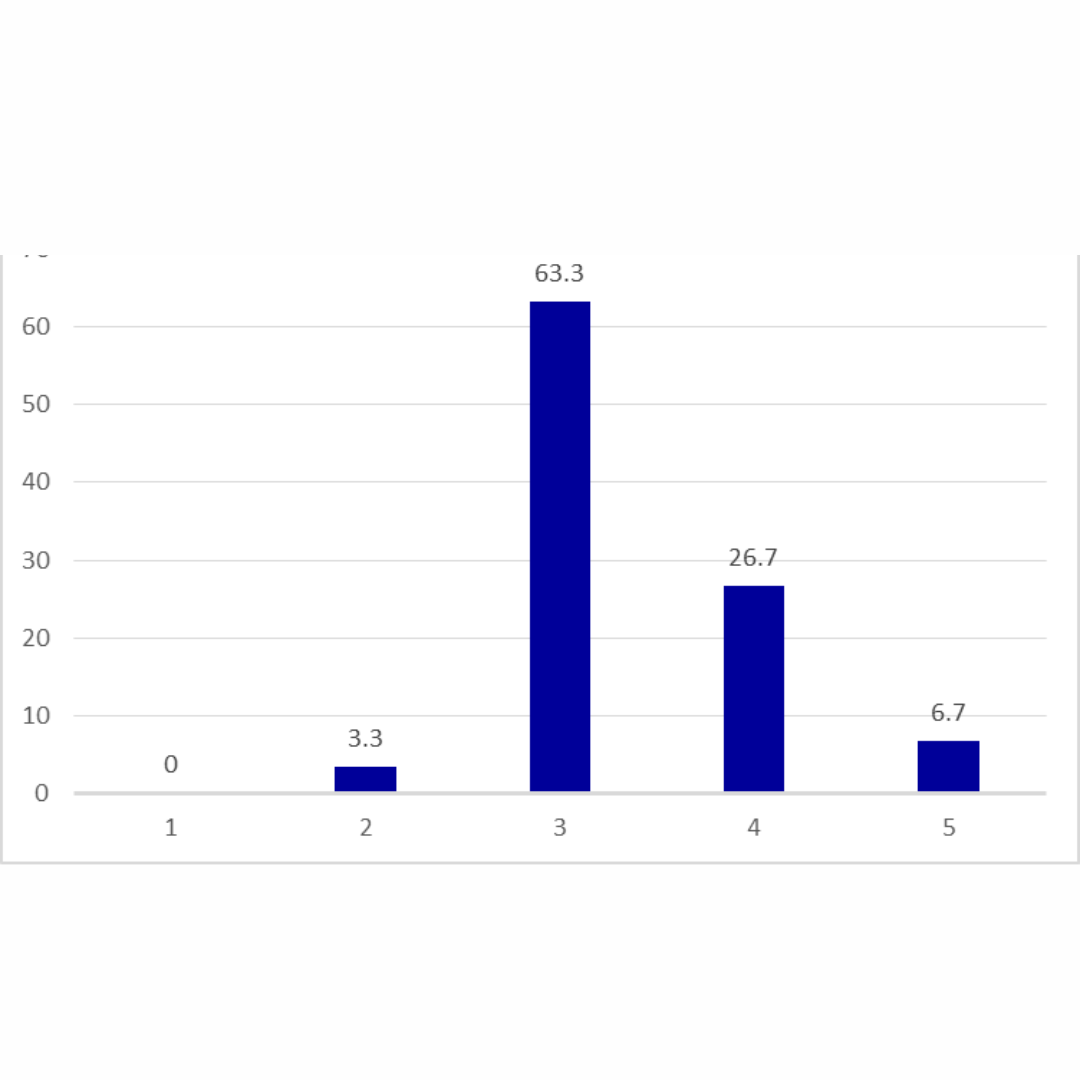
On a scale of 1-5, how much do you trust AI to securely manage and analyze your medical data for better healthcare outcomes?
Conclusion
These poll results are clearly indicating that the majority of people feel confident about AI-driven healthcare tools. This could be because of the growing trust in AI’s data-driven accuracy, efficiency, and ability to deliver results faster by processing huge data.
However, around 30% of the respondents are expressing partial trust. This could be because they can see the benefits of AI in healthcare but at the same time cannot trust the decision-making, and they might also be considering the empathy factor of humans.
A small percentage of the respondents are showing their distrust over AI-driven healthcare. This could be because of their fear about compromise with data security and biased algorithms, and they need more time to see and validate the impact of AI-driven tools.
Overall, this poll is showing that AI-driven healthcare solutions are gaining acceptance, but they can never replace human caregivers. AI-driven solutions should only be used for assisting the healthcare providers in giving more insights from the patient’s health data so that they can make better decisions on diagnosis and treatment. AI tools should also be used to lessen the burden of healthcare providers from routine, repetitive work so that they can spend quality time with patients.
How much of AI is too much in clinical diagnosis and treatment? We can say that AI and human intelligence should work together to provide better outcomes. AI should always stay as support, not replacement.